Technical Strategies

Causes and Effects
Deforestation in Haiti is driven by the pressing energy needs of a poverty-stricken population. Haitians resort to indiscriminate tree cutting to produce charcoal, a sought-after commodity for economic survival and cooking fuel. In 1923, over 60% of Haiti’s land was covered by forests, but by 2006, this figure dwindled to less than 2%, with even further depletion today. 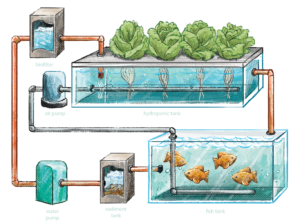 Unchecked deforestation results in the annual loss of approximately 15,000 acres (61 km2) of topsoil through erosion, damaging vital infrastructure like dams, lakes, irrigation systems, roads, and coastal marine ecosystems.
Unchecked deforestation results in the annual loss of approximately 15,000 acres (61 km2) of topsoil through erosion, damaging vital infrastructure like dams, lakes, irrigation systems, roads, and coastal marine ecosystems.
The consequences of unmitigated deforestation are severe, including lowered land productivity, exacerbated droughts, and eventual desertification. Haiti experiences recurrent natural disasters, and the uncontrolled watersheds from deforestation contribute to flooding in cities, leading to loss of life, traffic disruptions, damage to personal property, reduced agricultural output, and widespread unsanitary conditions.

insecurity vs Production
Solution Not Security
Aeroponics and modern husbandry techniques are revolutionizing sustainable agriculture by creating new pathways for fish farming, natural fertilizer production, and reforestation efforts. In aeroponics, plants are grown in an air or mist environment without soil, allowing for efficient nutrient delivery and water use. When integrated with fish farming, waste produced by fish can serve as a natural fertilizer for these aeroponic systems, enriching plant growth without synthetic chemicals. This closed-loop system not only supports healthier, more sustainable food production but also aids in reforestation by generating robust, nutrient-dense plants that can be used for replanting efforts, contributing to ecosystem restoration and biodiversity conservation.

Canal and potentials

